概念
-
HashRouter
它使用 URL 的哈希部分(即
window.location.hash)来保持页面的 UI 与 URL 同步。**重要说明:**哈希历史记录不支持
location.key或location.state。 -
BrowserRouter
使用 HTML5 历史 API( pushState,replaceState 和 popstate 事件),让页面的 UI 同步与 URL
区别
-
HashRouter 不需要服务器端渲染
服务器端无论对任何 URL 请求都返回一模一样的 HTML 就好,靠浏览器的 # 来区分 path 即可;BrowseRouter 则稍微复杂一点,因为要求服务器端对不同 URL 返回不同的 HTML
-
url 上表现不一致
比如,一个应用有两个页面 Home 和 About
如果用 HashRouter,两个 URL 就是这样,因为#后面的部分不会发给服务器,所以服务器只需要应对/路径的请求就好。
https://yourdomain.com/#/home // HashRouter https://yourdomain.com/#/about如果用 BrowserRouter,两个 URL 就是这样,服务器不得不应对/home 和/about 不同的请求。
https://yourdomain.com/home // BrowserRouter https://yourdomain.com/about
深层区别
hashRouter 不支持 location.key 、location.state
从其他资料来看,大多只有这一句说明,那如果项目使用了 hashRouter 之后不支持 location.key location.state 对应用有什么影响呢?
首先我们来看下在使用 BrowserRouter 或者 HashRouter 时是如何传递参数的。
在跳转路由的链接中通过 ‘?’ 传递参数
//link方式跳转
<Link to="/video/vue?msg=123">去关于我的页面 url传递参数</Link>
//js方式跳转
this.props.history.push({ pathname:"/video/vue?msg=123"});
about 中获取参数(props.location 中)
function About(props){
console.log(props)
return (<h2>about</h2>)
}

优缺点:参数比较灵活,参数直接在 url 中暴露,刷新路由页面时传递参数依然可以正常访问。缺点是还需要 js 通过 search 中解析类似 getParameter(msg)方式获取真实值
路由表中通过:id 方式
<Route path="/list/:id" component={List} />
<Link to="/list/123">列表</Link>
组件中接收传值
function List(props) {
console.log(props.match)
return <h2>List-Page</h2>;
}
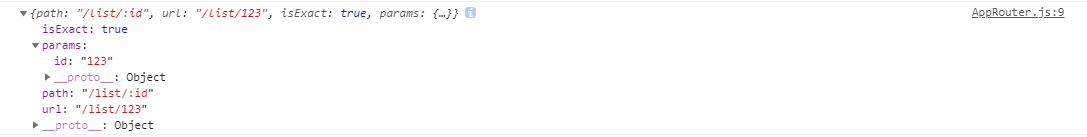
优缺点:参数比较灵活,参数直接在 url 中暴露,刷新路由页面时传递参数依然可以正常访问。但每增加一个参数需要在 Route 中注册一个,而且顺序需要一致。
其他 query(自定义属性)和 state
// query 传递参数 可使用其它字段名 效果一致
this.props.history.push({
pathname: '/about',
query: {
// 使用custom等亦可
msg: '来自首页的问候!by query',
},
})
// state 传递参数
this.props.history.push({
pathname: '/about',
state: {
msg: '来自首页的问候!by state',
},
})
// query 接受参数
console.log(this.props.location.query.msg) //来自首页的问候!by query
// state 接受参数
console.log(this.props.location.state.msg) //来自首页的问候!by state
优缺点:参数灵活,不用给 Route 额外的配置,参数是加密的,不暴露在 url 上。
以上测试结果方式对 HashRouter 和 BowserRouter 方式都有效
总结
不是找 HashRouter 和 BowserRouter 的区别吗?接下来再看…..通过 state 传参到 about 路由页面之后,刷新页面
跳转操作
this.props.history.push({
pathname: '/about',
state: {
msg: '来自首页的问候!by state',
},
})
HashRouter
//第一次进入页面打印结果
{"pathname":"/about","state":{"msg":"来自首页的问候!by state"},"search":"","hash":""}
//刷新页面或者后退再前进
{"pathname":"/about","search":"","hash":""}
BowserRouter
//第一次进入页面打印结果
{"pathname":"/about","state":{"msg":"来自首页的问候!by state"},"search":"","hash":"","key":"1m6gz4"}
//刷新页面或者后退再前进
{"pathname":"/about","state":{"msg":"来自首页的问候!by state"},"search":"","hash":"","key":"1m6gz4"}
到这儿,应该知道为什么说 location 不支持 key 和 state 了吧,当我们通过 state 传递参数的时候,因为 hashRouter 没有使用 html5 中 history 的 api,无法从历史记录中获取到 key 和 state 值,所以当刷新路由后 state 值会丢失导致页面显示异常(自定义属性两者都不能保存)。
实现路由页面页面刷新数据不丢失的方案
- BorwserRouter 有三种方式(url 传值,路由参数传值,以及 state)
- HashRouter 有两种方式(url 传值,路由参数传值)
- 本地缓存或者状态管理方案